2.2. Fluid Hydraulics
 |
2.2.3. Pressure Losses |

Task is intended to calculate mud flow parameters and pressure losses using mud properties, flow rate and
sections geometry.
Calculations are performed by sections and the number of section is not limited.
It provides a facility to compute pressure loss in whole the circulating system.
To calculate pressure losses in surface equipment it is necessary to create sections with equivalent diameter and
length.
Equivalent diameter must be defined in OD column (ID column shoud be kept as zero).
The same way should use for drill string sections - pipe inner diameter must be defined in OD column (ID column
shoud be kept as zero).
To calculate pressure loss in annulus define appropriate annular sections using OD column for hole size entry and
ID column for pipe outer diameter.
To finalize total pressure loss calculation it is required to compute and add pressure loss at bit (see Bit Hydraulics chapter).
Five rheological models are available (Bingham, Power Law, Herschel-Bulkley, API, Herschel-Bulkley (weighted avg.))
| Input Values |
 |
Mud Weight |
Density of Mud |
 |
Flow Rate |
Flow Rate provided by Pumps |
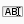 |
Rheological Model |
Mathematical model used to describe the flow behavior of mud |
 |
FANN Viscometer Dial Readings |
Fann Viscometer Dial Reading at 3, 6, 100, 200, 300, 600 revolutions per minute |
 |
Pipe Outer Diameter (OD) |
Use Hole Diameter for Annular Section or Pipe Inner Diameter to calculate inside Drill String |
 |
Pipe Inner Diameter (ID) |
Use Pipe Outer Diameter for Annular section or 0.0 to calculate inside Drill String |
 |
Pipe Length |
Section length |
| Results |
 |
Mud Velocity |
Velocity of mud inside section |
 |
Mud Critical Velocity |
Speed threshold above which the type of flow of the mud changes from laminar to turbulent |
 |
Reynolds Number |
Dimensionless number that gives a measure of the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces |
 |
Flow Type |
Type of flow of mud within the section |
 |
Pressure Loss |
Amount of pressure loss in all sections |